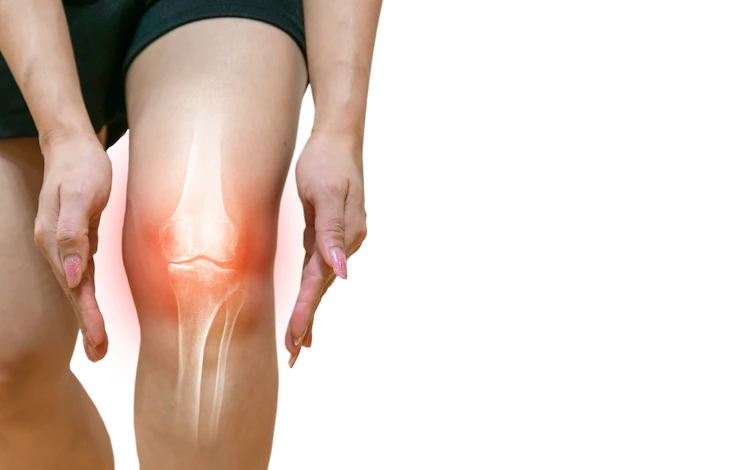
Dr Biren Nadkarni, Sr Consultant Orthopaedic and Joint Replacement Surgeon from Sitaram Bhartia Institute and Holy Family Hospital – New Delhi, shares information on knee join failure, cartilage decay and its remedies.
It was supposed to be a condition affecting the elderly. Until a few years ago, it was common knowledge that joint problems spared the young – but not anymore.
Over 15 million people worldwide suffer from knee joint failure each year due to the breakdown of surrounding cartilage in the joint. In India, 15% of the Indian population suffers from cartilage decay every year. It is projected that by 2030, an estimated 67 million Indians, aged 18 years or older, are to have doctor-diagnosed arthritis.
What is Cartilage?
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the human body, especially in the joints between bones. This tissue works to prevent the bones from rubbing against each other. Thus, cartilage acts as a cushion between joints. It prevents the bones from rubbing against each other (such as the bones in our knees and elbows) and also reduces friction in the joint with movement. It also holds some bones together, such as rib cartilage.
Cartilage also forms bone when you are growing – the ends of your long bones (arm and leg bones) are formed of cartilage when you are young, and this gradually changes into bone and grows longer.

What Do The Stats Say?
According to a study done at the University of London over 15 million people worldwide suffer knee joint failure each year due to the breakdown of surrounding cartilage in the joint.
Dr. Biren Nadkarni explained, “For every 1-unit increase in body mass index (BMI), the risk of rapid cartilage loss increased by 11%. Excess weight was a significant factor as well. The cartilage between our bones gets compressed by standing, sitting, and other daily activities as the day goes on. Degeneration of cartilage starts after the age of 40 years and above and sometimes earlier in case of injuries to the joint.”
Factors To Keep In Mind
Any factor (repeated trauma, advanced age, obesity etc.) that causes the breakdown of joint eventfully results in loss of joint shape and alignment. The ends of the bones then thicken and form bony growths called ‘spurs.’
Obesity is one of the factors that causes the cartilage to wear out early. Those having a sedentary lifestyle have weak muscles, resulting in the pressure of the body centering on the joints. This causes early depletion of cartilage.
Age-related changes in articular cartilage can contribute to the development and progression of osteoarthritis. These changes are most likely the result of an age-related decrease in the ability of chondrocytes (the main cells responsible for maintaining the cartilage) to maintain and repair the cartilage tissue. The cartilage covering bones in the joint region (called articular cartilage) undergoes thinning with age and activity, resulting in bone rubbing against bone, reduced movements, and pain. As the cushioning cartilage begins to break down from a lifetime of use, joints become inflamed and arthritic. Osteoarthritis affects the joints exposed to high stress (like the knee and hip) and is considered the result of daily wear and tear affecting the cartilage in the joints.
Symptoms That Signal Change
Dr. Biren Nadkarni lists some key changes in our body that act as signals for cartilage decay.
· It usually happens after the age of 40 and develops slowly over a period of years.
· It mainly affects the weight-bearing joints, like the knees and hips. However, it may also involve small joints of the fingers (in typists and computer operators, due to overuse of finger joints) and the spine (in old people).
· You will feel pain in the affected joint. The pain in the knees may become worse after suddenly rising from a prolonged sitting posture and sometimes in damp or rainy seasons (possibly due to a change in joint pressure with a change in atmospheric pressure.
· Early morning stiffness for not more than 30 minutes.
· Creaking in the affected joint and a grinding sensation with joint motion.
· Joints are usually cold as there is no inflammation.
· Does not affect the overall health of the person.
When To See A Doctor
Those above the age of 40 who are seeing the above mentioned symptoms should consult a doctor immediately. Pain in the joint on climbing stairs or on normal walking, stiffness in the joints, swelling in the joint, loss of movement and functional activities, and deformity in the joints are all signs you should consult with a specialis immediately.
Many of the changes in our cartilage result more from disuse than from simple aging. Regular exercises, stretching, maintaining healthy exercise habits, and maintaining weight helps improve our cartilage strength.